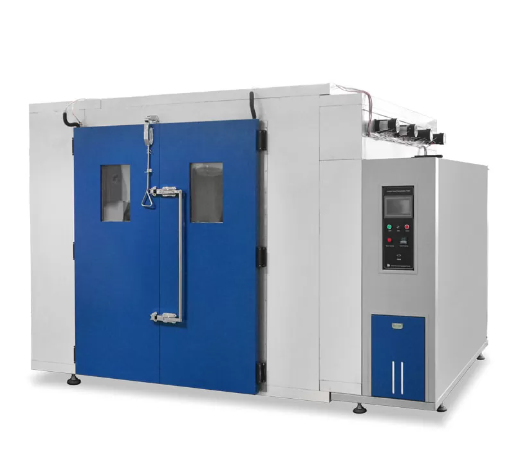
Uses of Industrial Oven
A look at some of the common applications for industrial ovens.
Industrial ovens are widely used in various industries such as food production, electronics, chemical processing, oil and gas, pharmaceutical, and automotive. Industrial ovens are basically heated chambers that are used for various industrial applications such as baking, curing, and drying parts, components or various products. These can be used for small or big volume applications, continuously with conveyor lines, in batches, and a range of different configurations, sizes, and temperatures.
More often than not, industrial ovens are used in other applications such as food productions, chemical processing, and electronics companies where circuit boards are run through the conveyor oven to attach the surface mount components.
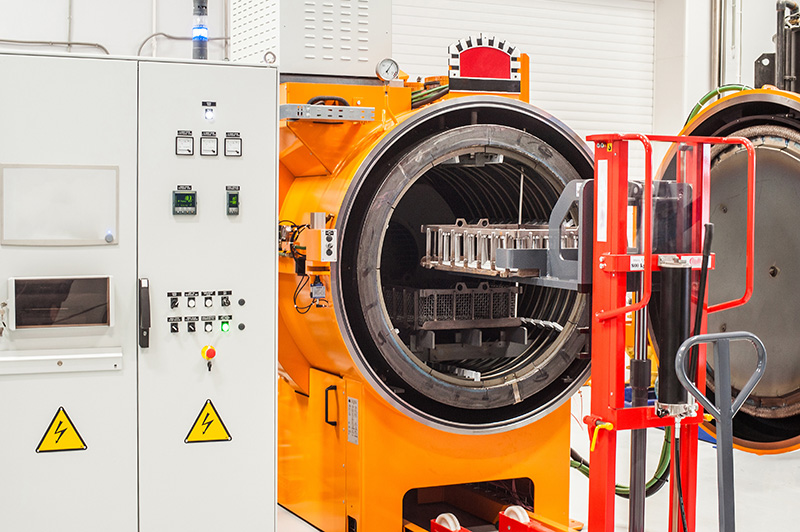
Some of the common applications of industrial ovens are as follows:
Sterilization of Medical Devices and Instruments
Industrial ovens can be used for sterilizing various medical devices and instruments. Other types of medical equipment that can be decontaminated using industrial ovens are medical and surgical components like staples and metal rods, scalpels, scissors, and syringes.
Industrial ovens that are used in the healthcare industry need the ability to control temperature accurately to ensure that all bacteria, microbes, viruses, and some contaminants that can be eliminated so medical equipment are safe to use.
Pharmaceutical Use of Industrial Ovens
When it comes to the pharmaceutical industry, oven innovation is deemed beneficial. It is because industrial ovens are used to bake the coatings of pills. Several industrial ovens are also used with thermal oxidizers to burn off the excess chemicals and waste made in the production of such products.
Burn-In Testing Materials
Industrial ovens can also be used for testing materials. For burn-in testing materials, the type of industrial ovens used is made for static and dynamic burn-in of integrated circuits and some electronic devices like laser diodes.
Drying Materials
Drying has multiple definitions and serves a lot of purposes. When it comes to pharmaceuticals, it may mean curing the tablets from a slurry. It may also refer to the sterilization of any laboratory equipment or it can be an industrial oven that comes as tower dryers or web dryers designed for coating, printing, and packaging.
Heat Treating Materials
Heat treating refers to the application of heat to metals to achieve the desired effect. Basically, it includes tempering, aging, stress relief, and annealing, which takes place at set temperatures that are dependent on the materials being treated.
Tempering is the procedure to lessen the hardened metal’s brittleness. It requires a controlled and stable environment to achieve the right balance of ductility and hardness. Stress relief, on the other hand, is the application of the heat to relieve structural, residual, and thermal stresses, which result from gas cutting, welding, shearing, and cold working.
In terms of aging in heat-treating materials, it stimulates the effect of the time on the materials. For instance, in aluminum materials, aging hardens the materials to increase their durability. To avoid cracking and damage, the process requires steady and low temperatures that may take place for days or hours. To increase the ductility of the materials, annealing is basically the process to apply heat to the materials.
Industrial Ovens for Sintering
It’s the process in which materials are compacted and bonded without reaching the melting point. With this process, the materials increase strength and gain density. Used in various industries such as metal injection molding, dental industry, and metallurgy, the sintering process basically includes cool-down, high heat, and pre-heating.
Common Types of Industrial Ovens
Not all industrial ovens are made equal. They vary from one type to another. Below are some of the common types of industrial ovens you should know:
- Drying Industrial Ovens – These are designed to get rid of any moisture from the raw materials placed within. This type of industrial oven undertakes a 3-step process, which includes heat-up, soak, and cool-down stage. The heat-up stage is where the materials are heated to the required temperature to get rid of the moisture in a set time. The soak stage is where materials are left to be soaked in the heat for a particular amount of time. The cool-down stage is where heated air is used and cooler air is fed in.
- Curing Industrial Ovens – These industrial ovens perform the process of curing, which is a heat-treatment used for accelerating the chemical reaction. Industrial curing ovens are used in several applications with some raw materials such as rubber, adhesives, and coatings.
- Batch Industrial Ovens –Different heat processes may be done in batch industrial ovens and these include aging, drying, curing, and annealing. Depending on your production needs, the batches of the raw materials may be placed in the industrial oven on racks, trucks or carts.
- Continuous Industrial Ovens – These industrial ovens are a perfect choice for the mass production of the same raw materials in a specific heat treatment process. When compared to other industrial ovens, they have separate cooling and heating chambers.
Conclusion
With the different applications where industrial ovens are used, it is important to note that industrial ovens are not the same with toaster or usual cooking ovens. That is why you have to determine your needs first before you decide to buy an industrial oven. If you are confused with the available options, it’s best to ask for assistance from the experts in industrial ovens for you to choose the right and best one for your unique requirements.